Mechanical properties of materials
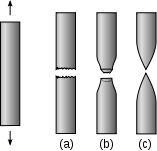
On this earth there are many materials available and each posses its own properties like Physical properties , chemical Properties and mechanical properties.
Mechanical properties are those which describe the behavior of material under different forces. properties like ductility , elasticity ,plasticity, brittleness, resilience , toughness , hardness , hardenability , strength , tensile/compressive strength , fatigue strength.. Although these terms seem similar, there are some small key differences.
Before going to understand these topics , you must have to idea on stress, strain , strain-curve
Ductility
It is the property of materials to deform into long thin wires without undergoing fracture .
Elasticity
This is the property of material to regain its original shape when external force is removed from it.
Stiffness
is the resistance of an object or material to deformation in response to an applied force. It is a measure of the object’s or material’s rigidity. A stiff object or material will resist deformation more than a less stiff object or material
Plasticity
The property of material to undergo permanent deformation . The body don’t regain its original shape even the external load is removed.
Brittleness
The property of material to get fracture without undergoing any elongation or contraction . Materials like Glass , most ceramics(Bricks, tiles ) are good examples of brittle materials.
Toughness
Toughness is the ability of material to absorb energy and plastically deform without undergoing fracture . Toughness contains both strength and ductile properties.
High strength material exhibits high resistance to force up-to some extent , after it will get fracture rather than elongating.
High ductile materials can get deformation easily , but they will elongate longer without getting fracture.
So, Tough materials exhibit high strength up-to elastic limit , also these exhibit high resistance to fracture after deformation

Resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy and return to its original shape without permanent deformation. It is a measure of the material’s toughness
Hardness
Hardness is the resistance of a material to localized surface deformation, such as a cuts or scratch. It is not the same as strength; a material can be very hard but not necessarily strong.
It is influenced by the strength of the interatomic bonds in the material. A hard material has strong interatomic bonds that make it difficult for indenters to penetrate the surface.
Hardenability
It is a measure of how much of a material can be hardened through heat treatment. It is influenced by the composition and microstructure of the material. Materials with high hardenability can be hardened to a greater depth than materials with low hardenability.
Tensile strength
The maximum amount of tensile(pulling) stress at which a material can withstand without fracture.
Compressive Strength
The maximum compressive (pushing) stress a material can withstand without failure.
Fatigue strength
It is ability of material to withstand cyclic loads ( loading and unloading continuously) without failure. It is important because , suppose a material can withstand at stress say 250 MPa , but this stress limit (tensile strength ). This strength will decrease as usage cycles increase . As we use the material ( no of cycles increases) the tensile strength will decrease .
- The endurance limit is the maximum stress that a material can withstand for an infinite number of loading cycles without failing. It is also known as the fatigue limit.
Few materials like steel and titanium alloys exhibit constant endurance limit. Whereas materials like aluminium alloys and copper alloys don’t have constant endurance limit.
- fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading.
- Failure of material due to fatigue is called Fatigue failure



